“Whenever any barrier stands between you and the full rights and dignity of citizenship, we must work to remove it, in the name of simple decency and justice. The promise of the ADA…has enabled people with disabilities to enjoy much greater access to a wide range of affordable travel, recreational opportunities and life-enriching services.”
President George W. Bush, New Freedom Initiative, February 1, 2001
Accessible Miniature Golf Courses
The recreation facility guidelines described in this guide focus on newly designed or newly constructed and altered miniature golf courses, adventure-style courses, and other putting courses. Other provisions contained in ADAAG address elements commonly found at a miniature golf course facility, such as accessible vehicle parking spaces, exterior accessible routes, and toilet and bathing facilities. ADAAG addresses only the built environment (structures and grounds). The guidelines do not address operational issues. Questions regarding operational issues should be directed to the Department of Justice, 1-800-514-0301 or 1-800-514-0383 (TTY).
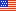
Accessible Holes
At least 50 percent of the holes on a miniature golf course must be accessible—if possible, operators should make all holes accessible. Accessible holes must be consecutive, to offer a more socially integrated experience. If only the minimum number of holes are accessible, it is recommended that designers select holes that will offer golfers who use wheelchairs or other mobility devices a playing experience that is as equivalent as possible to the experience of golfers without disabilities. An exception permits courses to have one break in the sequence of accessible holes, if the last hole in the sequence is the last hole on the course. The route in which a golfer with a disability must travel may not require travel back through any holes, even if the route is adjacent to the hole and not on the hole itself.
Click on diagram to view enlargement.
Accessible Routes
Accessible routes are continuous, unobstructed paths connecting all accessible elements and spaces of a building or facility. The accessible route must comply with ADAAG provisions for the location, width (minimum of 36 inches), passing space, head room, surface, slope (maximum of 1:12 or 8.33%), changes in level, doors, egress, and areas of rescue assistance, unless otherwise modified by specific provisions outlined in this guide. The accessible route must connect the facility’s entrance with the first accessible hole and with start of play area on each following accessible hole. The course must be configured to allow an easy exit from the last accessible hole to the facility exit or entrance. When not all holes are accessible, a player cannot be required to double back through holes to exit. Where possible, designers and operators are encouraged to make all holes accessible. An accessible route connecting accessible holes may be on the hole-playing surface or adjacent to it.
Accessible Routes on the Playing Surface
The surface of the accessible route must be stable, firm and slip
resistant. (Where carpets are used on the playing surface, they are not
required to comply with the requirements in ADAAG for accessible
carpets; however, they are still required to be stable, firm, and slip
resistant.)
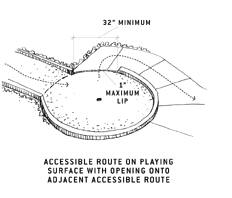
There is usually a curb around a hole to keep the ball within the area. When the accessible route is provided on the course, a 1-inch high maximum curb is permitted for an opening of 32 inches minimum where the accessible route extends outside the hole. This opening will permit passage of wheelchairs, while containing the ball within the hole. Designers should consider locating this opening in an area where the ball is not likely to roll.
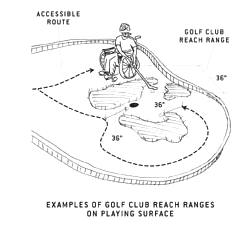
The accessible route on a playing surface must be within 36 inches (the golf club reach range) of any area where the ball comes to rest.
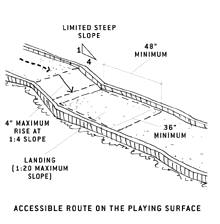 Landings must be 48 inches long. Where ramps change
direction, the landing size must be a minimum of 48 inches by 60 inches.
The orientation of the length and the width have not been specified for
added flexibility in design. Slopes on landings must be no more than
1:20 (5%).
Landings must be 48 inches long. Where ramps change
direction, the landing size must be a minimum of 48 inches by 60 inches.
The orientation of the length and the width have not been specified for
added flexibility in design. Slopes on landings must be no more than
1:20 (5%).
If the accessible route is on the playing surface, handrails are not required. The accessible route may include a maximum slope of 1:4 (25%) for a maximum 4-inch rise. These steeper slopes or ramps are permitted for limited distances.
Accessible Routes Adjacent to the Playing Surface
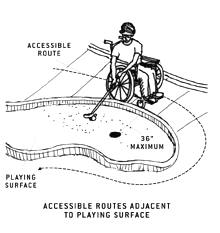 If the accessible route is adjacent to the playing surface, it must not
exceed 36 inches from any area where golf balls rest. This allows
players to be close enough to reach the ball and play from outside the
hole. The accessible route should be as close to the level playing areas
as possible.
If the accessible route is adjacent to the playing surface, it must not
exceed 36 inches from any area where golf balls rest. This allows
players to be close enough to reach the ball and play from outside the
hole. The accessible route should be as close to the level playing areas
as possible.
The accessible route adjacent to the playing surface must comply with ADAAG. The accessible route provisions in ADAAG address slope (maximum of 1:12 or 8.33%), width (minimum of 36 inches), cross slope (maximum of 1:50 or 2%), handrails, and changes in level.
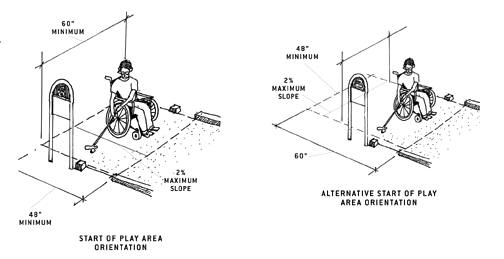
Start of Play Areas
The clear floor or ground space area at the start of play for each accessible hole must be 48 by 60 inches minimum to allow players to position themselves for the first shot. It must have a slope no steeper than 1:48 so that people using wheelchairs or mobility devices do not have to hit the ball while positioned on a sloped surface. The accessible route and the clear space can overlap.
Provision Index
This table highlights the sections of the ADA and ABA Accessibility Standards discussed in the amusement rides guide.
| ADA Standards* | ABA Standards | |
| Definitions | 106.5 | F106.5 |
| Cross Slope | 106.5 | F106.5 |
| Curb Ramp | 106.5 | F106.5 |
| Facility | 106.5 | F106.5 |
| Ramp | 106.5 | F106.5 |
| Running Slope | 106.5 | F106.5 |
| Miniature Golf Facilities (where provided) | 239 | F239 |
| Course Configuration | 239.3 | F239.3 |
| Holes (minimum number accessible) | 239.2 | F239.2 |
| Accessible Routes (where required) | 206 | F206 |
| Miniature Golf Course (specific provision) | 206.2.16 | F206.2.16 |
| Accessible Routes Components (typically used) | ||
| Curb Ramps | 406 | 406 |
| Doors and Gates | 404 | 404 |
| Ramps | 405 | 405 |
| Walking Surfaces with Running Slopes of 5% or less | 403 | 403 |
| When on Playing Surfaces (exceptions) | 1007.2 EXs | 1007.2 EXs |
| EX 1 - Surface exception (for 302.2) | 1007.2 EX 1 | 1007.2 EX 1 |
| EX 2 - Curb exception (1 inch) | 1007.2 EX 2 | 1007.2 EX 2 |
| EX 3 - Slope exception (1:4) | 1007.2 EX 3 | 1007.2 EX 3 |
| EX 4 - Landing slope exception (1:20) | 1007.2 EX4 | 1007.2 EX4 |
| EX 5 - Landing length exception (48 inches) | 1007.2 EX5 | 1007.2 EX5 |
| EX 6 - Landing size exception (48 inches by 60 inches) | 1007.2 EX6 | 1007.2 EX6 |
| EX 7 - Handrail exception | 1007.2 EX7 | 1007.2 EX7 |
| Technical Requirements for Miniature Golf Holes | 1007.3 | 1007.3 |
| Golf Club Reach Range | 1007.3.2 | 1007.3.2 |
| Start of Play | 1007.3.1 | 1007.3.1 |
| Other Typical Scoping Requirements at Fishing Facilities | ||
| Dining surfaces | 226 | F226 |
| Employee Work Areas (exception) | 203.9 | no similar exception |
| Parking | 208 | F208 |
| Passenger Loading Zones and Bus Stops | 209 | F209 |
| Sales and Service Counters | 227.3 | F227.3 |
| Signage | 216 | F216 |
| Toilet and Bathing | 213 | F213 |
| Vending Machines | 228 | F228 |
* The guide uses the term ADAAG (Americans with Disabilities Act Accessibility Guidelines) as the basis of the requirements discussed. The recreational provisions of these guidelines were adopted into the 2010 ADA Standards without changes, so the ADAAG section numbers correspond to the same section numbers in the ADA Standards (as well as the Architectural Barriers Act (ABA) Accessibility Standards).